-
Jan 25, 2025 |  mdpi.com | Xiaoyu Zhang |Zhenhua Wang |Jian Liu |Wenhao Li
mdpi.com | Xiaoyu Zhang |Zhenhua Wang |Jian Liu |Wenhao Li
All articles published by MDPI are made immediately available worldwide under an open access license. No special permission is required to reuse all or part of the article published by MDPI, including figures and tables. For articles published under an open access Creative Common CC BY license, any part of the article may be reused without permission provided that the original article is clearly cited. For more information, please refer to https://www.mdpi.com/openaccess.
-
Jan 10, 2025 |  onlinelibrary.wiley.com | Xiaoyu Zhang |Hai Wang
onlinelibrary.wiley.com | Xiaoyu Zhang |Hai Wang
Conflicts of Interest The authors declare no conflicts of interest. Supporting Information Filename Description inm13502-sup-0001-FigureS1-S5.pdfPDF document, 1.7 MB Figure S1. References , , and . 2021. “Effect of Repeated Simulation Experience on Perceived Self-Efficacy Among Undergraduate Nursing Students.” Nurse Education Today 106: 105057. , , , , , and . 2023.
-
Dec 2, 2024 |  nutritionandmetabolism.biomedcentral.com | Hui Wang |Yuxin Chen |Yang Chen |Yixi Xu |Xiaoyu Zhang |Qingyang Mao | +7 more
nutritionandmetabolism.biomedcentral.com | Hui Wang |Yuxin Chen |Yang Chen |Yixi Xu |Xiaoyu Zhang |Qingyang Mao | +7 more
This investigation adopted a two-center case–control study in China. Detailed information about the study design and participant recruitment can be found in our previous publications [17,18,19]. In brief, the present study comprised 195 patients diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), of which 83 exhibited DR and 112 did not.
-
Nov 26, 2024 | 00445-8&sz=64) cell.com | Kevin Scott |Hiroyuki Kojima |Nathalie Ropek |Charles Warren |Tiffany Zhang |Simon Hogg | +9 more
cell.com | Kevin Scott |Hiroyuki Kojima |Nathalie Ropek |Charles Warren |Tiffany Zhang |Simon Hogg | +9 more
Keywordscovalent immunomodulatorsactivity-based protein profilinginterleukin-2-inducible T-cell kinasealternative splicingsplicing factor 3b subunit 1Get full text accessLog in, subscribe or purchase for full access. References1. Lynch, K.W.Consequences of regulated pre-mRNA splicing in the immune systemNat. Rev. Immunol. 2004; 4:931-9402. Martinez, N.M. ∙ Pan, Q. ∙ Cole, B.S. ... Alternative splicing networks regulated by signaling in human T cellsRNA. 2012; 18:1029-10403. Pan, Q. ∙ Shai, O.
-
Nov 25, 2024 |  genomebiology.biomedcentral.com | Wenxi Wang |Zihao Wang |Zhe Chen |Xiaoyu Zhang |Zhen Qin |Lingfeng Miao | +10 more
genomebiology.biomedcentral.com | Wenxi Wang |Zihao Wang |Zhe Chen |Xiaoyu Zhang |Zhen Qin |Lingfeng Miao | +10 more
Publisher Correction: Tagging large CNV blocks in wheat boosts digitalization of germplasm resources by ultra-low-coverage sequencing Publisher Correction Open access Published: 25 November 2024 Genome Biology volume 25, Article number: 298 (2024) Cite this article The Original Article was published on 01 July 2024 Correction: Genome Biol 25, 171 (2024) https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-024-03315-6 Following publication of the original article [1], the authors identified a typesetting error,...
-
Oct 29, 2024 |  mdpi.com | Ming Li |Wenjun Wang |Xiaoyu Zhang |Jing Hui Wang
mdpi.com | Ming Li |Wenjun Wang |Xiaoyu Zhang |Jing Hui Wang
All articles published by MDPI are made immediately available worldwide under an open access license. No special permission is required to reuse all or part of the article published by MDPI, including figures and tables. For articles published under an open access Creative Common CC BY license, any part of the article may be reused without permission provided that the original article is clearly cited. For more information, please refer to https://www.mdpi.com/openaccess.
-
Oct 17, 2024 |  mdpi.com | Heng Wang |Xu Feng Huang |Bing F. Wang |Xiaoyu Zhang
mdpi.com | Heng Wang |Xu Feng Huang |Bing F. Wang |Xiaoyu Zhang
All articles published by MDPI are made immediately available worldwide under an open access license. No special permission is required to reuse all or part of the article published by MDPI, including figures and tables. For articles published under an open access Creative Common CC BY license, any part of the article may be reused without permission provided that the original article is clearly cited. For more information, please refer to https://www.mdpi.com/openaccess.
-
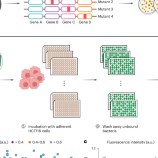
Aug 6, 2024 |  frontiersin.org | Xiaoyu Zhang |Deng Zhang |Xin Zhang |Xifan Zhang
frontiersin.org | Xiaoyu Zhang |Deng Zhang |Xin Zhang |Xifan Zhang
The diagnosis and treatment of bacterial infections in the medical and public health field in the 21st century remain significantly challenging. Artificial I...
-
Jun 1, 2024 |  onlinelibrary.wiley.com | Jia Wang |Xiaoyu Zhang |Shuqin Li |Yajie Wang
onlinelibrary.wiley.com | Jia Wang |Xiaoyu Zhang |Shuqin Li |Yajie Wang
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
-
Apr 13, 2024 |  nature.com | Yifan Xu |Jingrong Wang |Jianwei Shi |Suhang Song |Xiaoyu Zhang |Xiaohan Teng | +3 more
nature.com | Yifan Xu |Jingrong Wang |Jianwei Shi |Suhang Song |Xiaoyu Zhang |Xiaohan Teng | +3 more
As an integral part of the overall life cycle, it is crucial to ensure equity and accessibility to palliative care services at the end of life. The knowledge of healthcare providers has a significant beneficial impact on the quality of palliative care services. This study aimed to compare the nationwide geographic distribution of healthcare providers’ knowledge of palliative care at the provincial level in China and identify the possible factors associated with its geographic disparities. A descriptive cross-sectional study was conducted in all provinces (n = 29) that implemented palliative care pilot programs in China. Data were collected online using a structured questionnaire. The possible factors associated with healthcare providers’ knowledge including economy, demographics, and health, were explored by using exploratory regression and ordinary least squares. In addition, spatial autocorrelation was also examined with Moran’s I, LISA, and Geographically Weighted Regression. A total of 18,272 participants from 903 health institutions in 87 palliative care pilot cities were included across 29 out of 31 provinces in China. The average knowledge score (mean ± standard deviation [SD]) was 8.61 ± 2.85. A positive spatial correlation was observed in healthcare providers’ palliative care knowledge level in China. The high level of knowledge was significantly associated with fewer hospitals per 10,000 population (β = −0.384, 95% CI: −0.601 to −0.168, p = 0.001), more primary healthcare institutions per 10,000 population (β = 0.220, 95% CI: 0.032–0.407, p = 0.024), and more community health center visits (β = 0.259, 95% CI: 0.054–0.465, p = 0.016), with higher coefficients being observed in the northwest and northeast regions. This study suggested that the knowledge level of palliative care among healthcare providers nationwide was relatively low, indicating the existence of a disparity between the supply and demand of palliative care services. There may be regional disparities in palliative care services based on the substantial geographical variation in healthcare provider knowledge, emphasizing the necessity of tailored interventions targeting areas with the greatest need.
mdpi.com | Xiaoyu Zhang |Zhenhua Wang |Jian Liu |Wenhao Li
onlinelibrary.wiley.com | Xiaoyu Zhang |Hai Wang
nutritionandmetabolism.biomedcentral.com | Hui Wang |Yuxin Chen |Yang Chen |Yixi Xu |Xiaoyu Zhang |Qingyang Mao | +7 more
cell.com | Kevin Scott |Hiroyuki Kojima |Nathalie Ropek |Charles Warren |Tiffany Zhang |Simon Hogg | +9 more
genomebiology.biomedcentral.com | Wenxi Wang |Zihao Wang |Zhe Chen |Xiaoyu Zhang |Zhen Qin |Lingfeng Miao | +10 more